Range Check
The “Range check” offers the possibility to check if a value of the signal is within a certain range. It is possible to specify a substitute value if the limit value / allowed range is violated.
Configuration
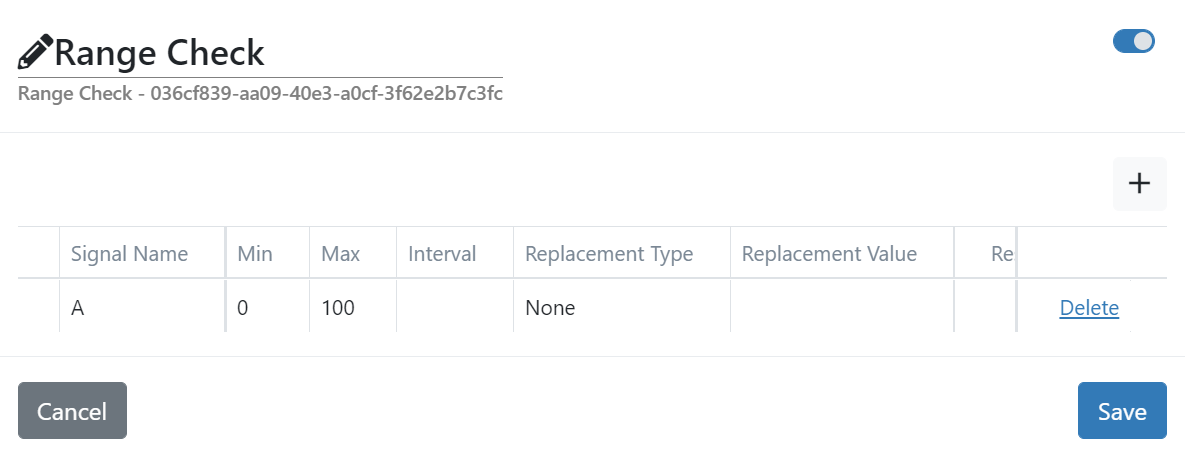
- Signal Name
The name of the signal at the ‘in’ port.
- Min (optional)
The minimum value allowed (\(x \geq min\)) (not checked if empty). The value can be a floating point value or a signal expression (
{signalName}).- Max (optional)
The maximum allowed value (\(x \leq max\)) (not checked if empty). The value can be a floating point value or a signal expression (
{signalName}).- Interval (optional)
The mathematical specification of the allowed ranges.
- Example 1:
Signal lowerLimit=3
[{lowerLimit},10]\(3 \leq x \leq 10\)
- Example 2:
[5,10];]100,300]\(5 \leq x \leq 10 \lor 100 < x \leq 300\)
see interval
- Replacement Type
- Options:
None No replacement will be made.
Value The current value will be replaced by the ‘Replacement Value’.
Violated Limit The current value will be replaced with the violated limit.
- Example:
The upper limit 1000 has been violated. The replacement value will be 1000.
Warning
This option can only be used, if the range check does not use Interval.
- Replacement Value (optional)
The value to replace when a limit is violated (used only if Replacement Type is Value). The value can be a floating point number or a signal expression (
{signalName}).- Reset Flags
If true the violation flags (UpperLimitViolated,LowerLimitViolated) are reset.
- Reset Quality
Normally the quality of the value automatically becomes bad if the allowed range is violated. If this value is set to true, the original quality is preserved.